Introduction
In today’s fast‑moving world of precision manufacturing, the choice of a gear reducer can make or break the performance of a CNC machine tool. Whether you’re fitting a new lathe, upgrading a milling center, or building a custom robotic work cell, the right reducer delivers smooth motion, high torque, and long life. Drawing from more than a decade working directly with CNC shops and suppliers, this article breaks down the practical steps that help engineers and shop managers pick the best gear reducer for their specific needs.
What Is a Gear Reducer?
A gear reducer is a mechanical device that transforms the input speed and torque from a motor into a reduced speed and increased torque at the output shaft. In CNC applications, this allows a small, high‑speed electric motor to drive hard‑cutting tools, spindle heads, or servo drives, while keeping the overall system compact and energy efficient.
Common types of reducers used in CNC machines include:
- Spur reduction gearboxes – simple, reliable, and ideal for low‑speed, high‑torque tasks.
- Planetary gearboxes – offer higher torque density and smoother operation, perfect for high‑precision axes.
- Helical or bevel gear systems – provide quiet, low‑vibration performance, often used in cutting tools.
- Synchromesh transmission – for applications requiring precise gear synchronization and quick shifts.
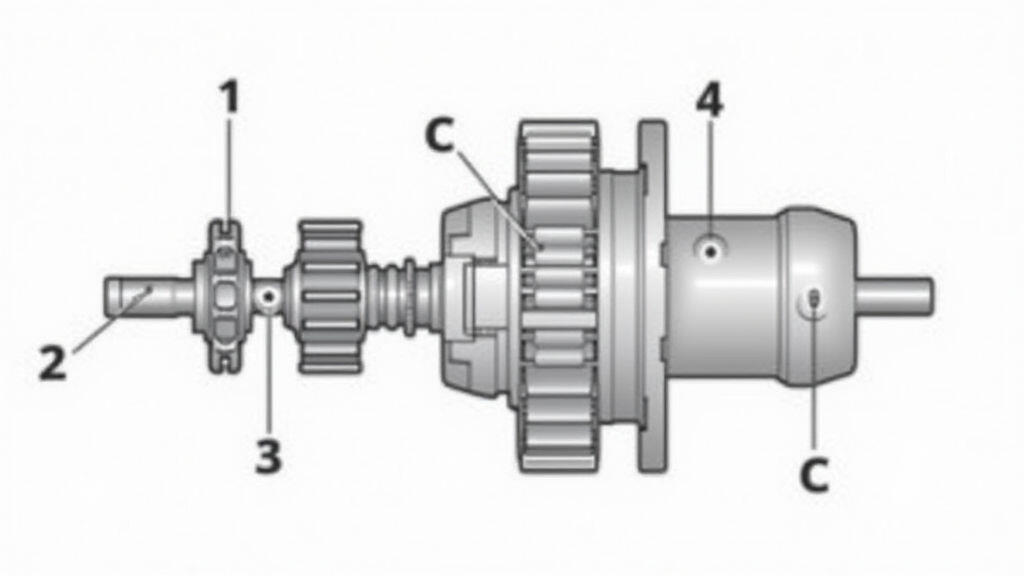
Key Factors in Gear Reducer Selection
Choosing the right reducer involves balancing several engineering and business considerations. Below are the most critical factors to evaluate:
- Reduction Ratio
Determine the required output speed and torque for your CNC axis. A higher reduction ratio increases torque but reduces speed. A quick look-up table for a typical 100 mm/s spindle speed can help estimate the needed ratio.
- Torque Capacity
Make sure the reducer can deliver the peak torque you will impose during cutting, holding, or acceleration. Include a 10‑20 % safety margin for spikes and shock loads.
- Mechanical Efficiency
Higher efficiency (above 85 %) means less heat and less energy waste. Pay special attention to gear type and lubricant quality.
- Life Expectancy & Reliability
Industrial reducers must endure thousands of cutting cycles. Look for wear‑resistant gear teeth, proper material composition (e.g., alloy steel or hardened cast iron), and proven manufacturer warranties.
- Mounting & Size Constraints
Physical clearance, shaft alignment, and mounting patterns must fit your machine’s layout. An oversized reducer can stir up vibration or require costly redesign.
- Noise & Vibration
In many CNC shops, reduced noise improves productivity. Planetary gearboxes with precision gearing often offer significantly lower vibration.
- Cost & Total Ownership
While upfront price matters, consider maintenance costs, spare parts availability, and expected lifespan.
Matching Gear Reducer to CNC Application
Different CNC axes and components have distinct performance footprints. Here are a few common scenarios and the recommended gear solutions:
- X‑axis linear travel (high speed, low torque) – A 2–3 :1 planetary reducer from a 24 V DC motor often suffices.
- Z‑axis rotary spindle (high torque, high spindle speed) – A helical gear reducer with 20 :1 ratio and 50 Nm torque rating.
- Tool changer (fast, high precision) – A synchromesh reduction gearbox for smooth, reversible motion.
- Laser or CNC router (precise, high frequency) – Ultra‑quiet planetary gearboxes with damping housing to suppress chatter.
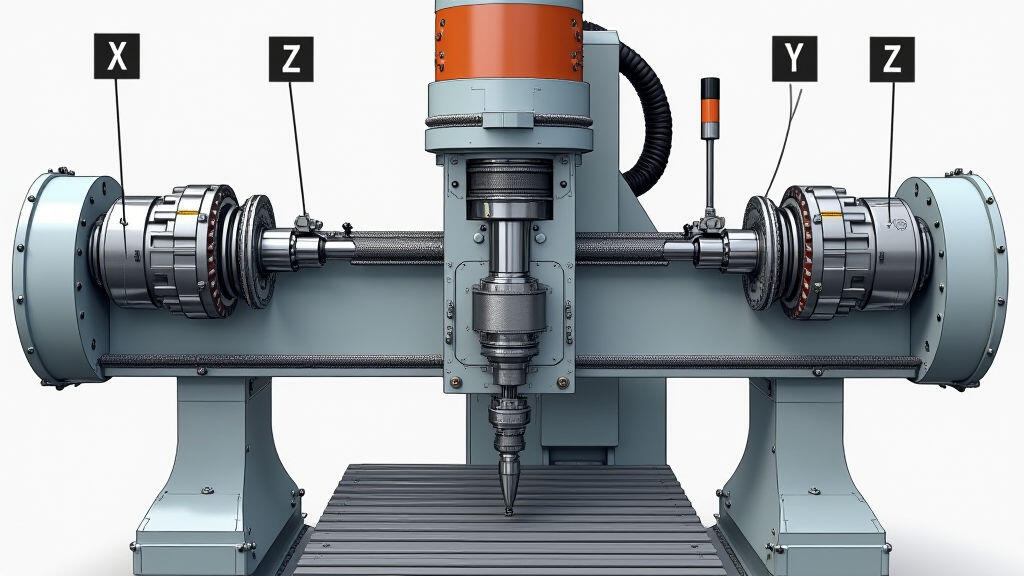
Case Study: Upgrading a 5‑Axis Machine
Last year, a midsized automotive supplier upgraded their 5‑axis machining center to meet stringent tolerances for new alloy components. The original axial reducers had been servos with a 4 :1 planet ratio. They were now over 8 years old, exhibiting increased vibration during deep cuts.
Engineers replaced the older units with 5 :1 helical reducers rated at 70 Nm, providing both higher torque and smoother output. They also switched the lubricant from routine oil to a synthetic, high‑temperature additive kit. After two weeks of operation, vibration monitoring dropped by 40 %. The machine also ran 10 % more efficiently, reducing power consumption.
Key takeaways: choose a ratio that meets torque needs with a safety margin, and use modern gear designs with improved lubrication to extend service life.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Over‑optimizing for cost – A cheap gear reducer may seem attractive but can lead to frequent breakdowns. Balance cost with reliability.
- Ignoring gear type compatibility – Mixing gear materials or styles (e.g., using a spur gear as a planetary reducer) can cause catastrophic failures.
- Neglecting alignment – Shaft misalignment forces uneven load distribution, shortening the reducer’s life; use precision bushings.
- Forgetting thermal management – Continual high‑speed operation can heat gear teeth. Ensure proper spacing and ventilation, or add an oil cooler if needed.
Future Trends in Gear Reducers for CNC
Emerging technologies are shaping the next wave of gear reducer design:
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing) – Allows complex tooth profiles for minimal vibration.
- High‑speed servo integration – Combining gear reducers with servo drives for real‑time torque control.
- Smart monitoring – Embedded sensors to track temperature, vibration, and torque for predictive maintenance.
- Environmentally friendly lubricants – Reducing waste and ensuring residue‑free operation for cleanroom CNC floors.
In the context of Industry 4.0, these features enable higher efficiency, reduced downtime, and real‑time data analytics – all of which translate to competitive advantage for machine shops and OEMs alike.
Conclusion
Choosing the right gear reducer is far more than a simple mechanical decision; it’s a strategic investment in performance, quality, and operational continuity. By systematically evaluating reduction ratio, torque capacity, efficiency, reliability, size constraints, noise, and cost, engineers can align the machine’s motion system with the specific demands of their production environment.
The real-world case studies underline how even modest upgrades to gear reducer design—better ratios, improved gear geometry, and superior lubrication—can drive measurable gains in precision, speed, and energy consumption.
As Industry 4.0 continues to emphasize interconnected, data‑driven production, the importance of smart, high‑performance gear reducers will only grow. Those who adopt advanced gear technologies now will be better positioned to meet tomorrow’s manufacturing challenges, ensuring higher throughput, lower maintenance costs, and sustained competitive advantage.




Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked